
Infographic: Advancing an Embodied Understanding of Accessibility for Persons with Disabilities
On this page, you will find the infographic ‘Advancing an Embodied Understanding of Accessibility for Persons with Disabilities’. You will find a text description of the infographic below, and an audio description at the bottom of the page.
Home » Creative Works » Infographics »
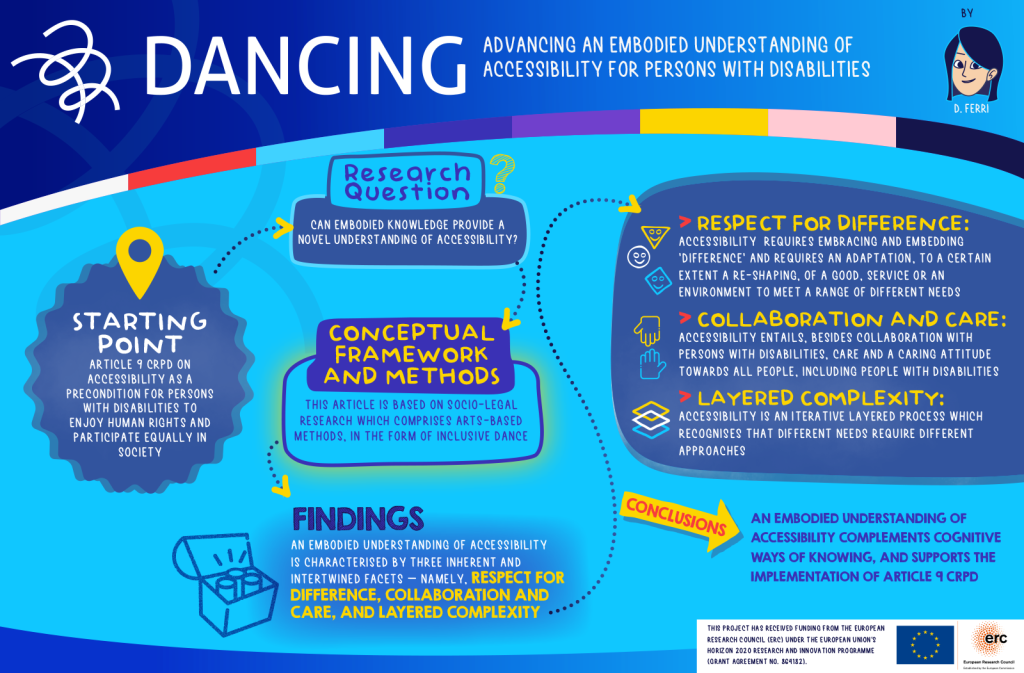
Infographic: Advancing an Embodied Understanding of Accessibility for Persons with Disabilities – Text Description
The infographic uses blues, white, and turquoise with accents of yellow, consistent with the earlier infographics. The mood of the design is playful and non-intimidating. There is the DANCING project logo in the top left-hand corner, and an acknowledgement to the European Research Council (ERC), the funding body, in the bottom right-hand corner. Text is shown in boxes and lozenges with arrows in between to suggest a flow of information. The text runs as follows:
Advancing an Embodied Understanding of Accessibility for Persons with Disabilities by D. Ferri
Starting Point
Article 9 CRPD on accessibility as a precondition for persons with disabilities to enjoy human rights and participate equally in society.
Research Question
Can embodied knowledge provide a novel understanding of accessibility?
Conceptual Framework and Methods
This article is based on socio-legal research which comprises arts-based methods, in the form of inclusive dance.
Findings
An embodied understanding of accessibility is characterized by three inherent and intertwined facets — namely, respect for difference, collaboration and care, and layered complexity.
- RESPECT FOR DIFFERENCE: accessibility requires embracing and embedding ‘difference’ and requires an adaptation, to a certain extent a re-shaping, of a good, service or an environment to meet a range of different needs.
- COLLABORATION AND CARE: accessibility entails, besides collaboration with persons with disabilities, care and a caring attitude towards all people, including people with disabilities.
- LAYERED COMPLEXITY: accessibility is an iterative layered process which recognises that different needs require different approaches.
Conclusions
An embodied understanding of accessibility complements cognitive ways of knowing, and supports the implementation of Article 9 CRPD.
The text concludes with an acknowledgement to the funder: This project has received funding from the European Research Council (ERC) under the European Union’s Horizon 2020 Research and Innovation programme (grant agreement no. 864182).


